Numeral System
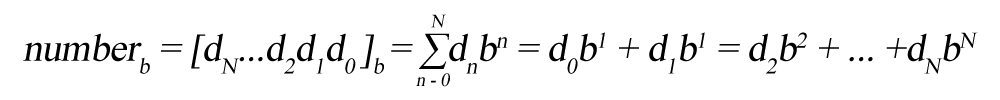
b – numeral system base
dn – the n-th digit
n – can start from negative number if the number has a fraction part.
N+1 – the number of digits
Binary Numeral System – Base-2
Binary numbers uses only 0 and 1 digits.
B denotes binary prefix.
For example:
11102 = 1110B = 1×24+1×23+1×22+0×21 = 16 + 8 + 4 = 28
111012 = 11101B = 1×24+1×23+1×22+0×21+1×20 = 16 + 8 + 4 + 1 = 29
1011002 = 101100B = 1×25+0×24+1×23+1×22+0×21+0×20= 32 + 8 + 4 = 44
Octal Numeral System – Base-8
Octal numbers uses digits from 0..7.
For examples:
368 = 3×81+6×80 = 24 + 6 = 30
508 = 5×81+0×80 = 40
24038 = 2×83+4×82+0×81+3×80= 1024 + 256 + 24 = 1304
Decimal Numeral System – Base-10
Decimal numbers uses digits from 0..9.
These are the regular numbers that we use.
For example:
114210 = 1×103+1×102+4×101+2×100 = 1000 + 100 + 40 + 2 = 1142
Hexadecimal Numeral System – Base-16
Hex numbers uses digits from 0..9 and A..F.
H denotes hex prefix.
For examples:
1416 = 14H = 1×161+4×160 = 16 + 4 = 20
3F16 = 3FH = 3×161+15×160 = 48 + 15 = 63
CB1216 = CB12H = 12×163+11×162+1×161+2×160= 49152 + 2816 + 16 + 2 = 51986
Numeral systems conversion table
| Decimal Base-10 | Binary Base-2 | Octal Base-8 | Hexadecimal Base-16 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 10 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 11 | 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 100 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 101 | 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 110 | 6 | 6 |
| 7 | 111 | 7 | 7 |
| 8 | 1000 | 10 | 8 |
| 9 | 1001 | 11 | 9 |
| 10 | 1010 | 12 | A |
| 11 | 1011 | 13 | B |
| 12 | 1100 | 14 | C |
| 13 | 1101 | 15 | D |
| 14 | 1110 | 16 | E |
| 15 | 1111 | 17 | F |
| 16 | 10000 | 20 | 10 |
| 17 | 10001 | 21 | 11 |
| 18 | 10010 | 22 | 12 |
| 19 | 10011 | 23 | 13 |
| 20 | 10100 | 24 | 14 |
| 21 | 10101 | 25 | 15 |
| 22 | 10110 | 26 | 16 |
| 23 | 10111 | 27 | 17 |
| 24 | 11000 | 30 | 18 |
| 25 | 11001 | 31 | 19 |
| 26 | 11010 | 32 | 1A |
| 27 | 11011 | 33 | 1B |
| 28 | 11100 | 34 | 1C |
| 29 | 11101 | 35 | 1D |
| 30 | 11110 | 36 | 1E |
| 31 | 11111 | 37 | 1F |
| 32 | 100000 | 40 | 20 |
